알고리즘/그래프
[BOJ] 백준 7576 - 토마토 풀이
송승현(SSH)
2023. 3. 12. 22:08
1. 문제
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/7576
7576번: 토마토
첫 줄에는 상자의 크기를 나타내는 두 정수 M,N이 주어진다. M은 상자의 가로 칸의 수, N은 상자의 세로 칸의 수를 나타낸다. 단, 2 ≤ M,N ≤ 1,000 이다. 둘째 줄부터는 하나의 상자에 저장된 토마토
www.acmicpc.net
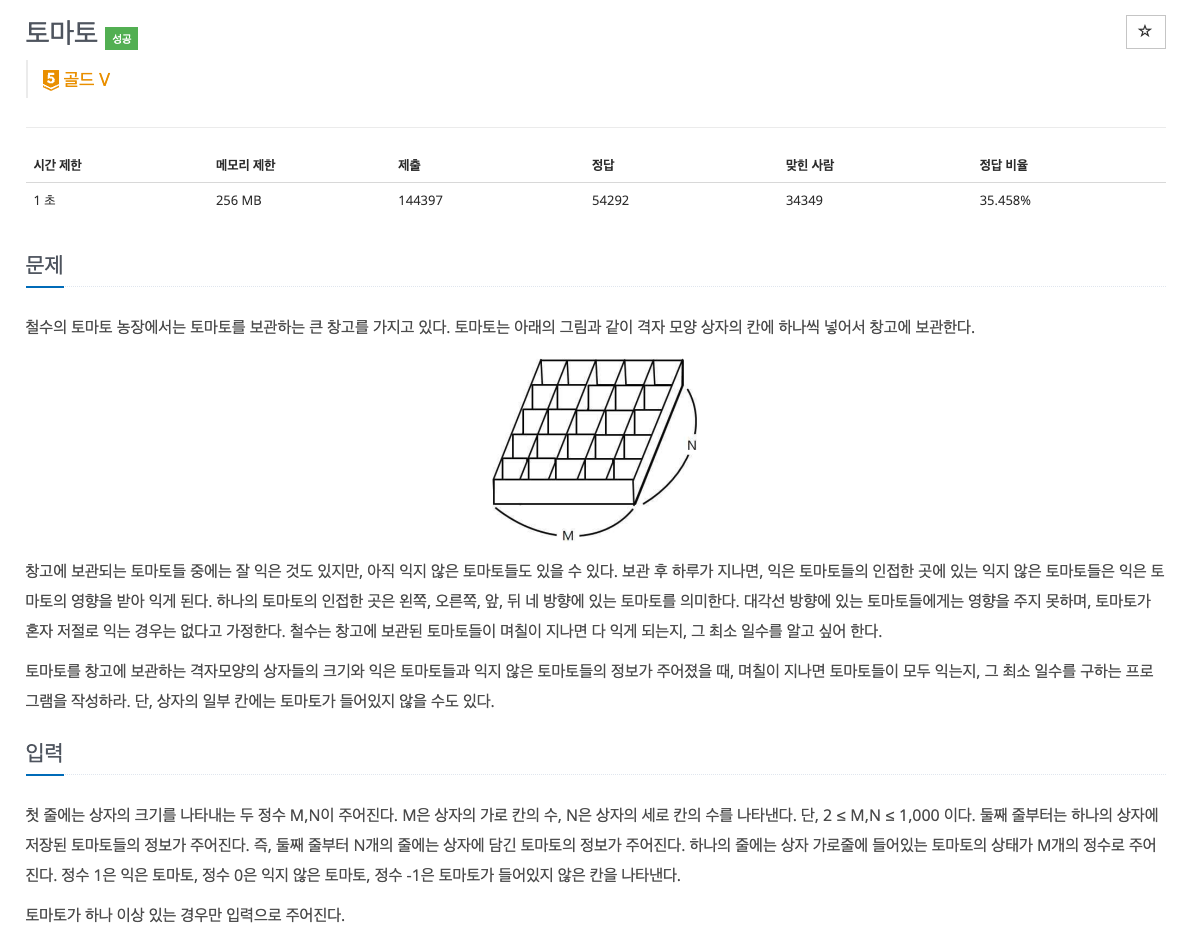

2. 풀이 Point
<Error Point>
- 익은 토마토가 처음에 여러개가 있을 경우 동시에 진행됨을 간과함
<풀이 Point>
- 입력을 받을 때 처음 익은 토마토의 좌표를 미리 queue에 넣어두고 그곳을 방문처리한다.
- 처음 입력을 받았을 때 모두 익어있을 경우가 있으므로, 이를 탐색한다
- 그 후 BFS 탐색을 진행하면서 토마토가 익는 경우와 익는 day를 갱신한다.
- 탐색을 마쳤을 때 안 익은 토마토가 있는 경우 -1
3. 소스 코드
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
static int M, N;
static int[][] tomatoBox;
static int[] dx = {1, -1, 0, 0};
static int[] dy = {0, 0, -1, 1};
static boolean[][] visited;
static class Point {
int x;
int y;
int day; // 좌표의 토마토가 익을때까지 걸린 day
public Point(int x, int y, int day) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.day = day;
}
}
// bfs를 탐색할 큐
static Queue<Point> q = new LinkedList<>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(System.out));
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
N = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
tomatoBox = new int[N][M];
visited = new boolean[N][M];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
tomatoBox[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken());
// 이미 익은 토마토일 경우
if (tomatoBox[i][j] == 1) {
q.add(new Point(i, j, 0));
visited[i][j] = true;
}
}
}
// 0인지 탐색 : 이미 익을 수 있는 토마토가 다 익은 경우
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (tomatoBox[i][j] == -1 || tomatoBox[i][j] == 1) {
cnt += 1;
}
}
}
int result = 0;
// 0인지 탐색 : 이미 익을 수 있는 토마토가 다 익은 경우 0을 입력
if (cnt == N * M) {
result = 0;
} else {
result = tomatoBFS();
// 하나라도 익지 못한 토마토가 있을 경우
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) {
if (tomatoBox[i][j] == 0) {
result = -1;
}
}
}
}
bw.write(Integer.toString(result));
bw.flush();
bw.close();
br.close();
}
private static int tomatoBFS() {
// 토마토가 익는 day의 최대 값
int dayMax = 0;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Point poll = q.poll();
// 지금까지 갱신한 날짜와 큐에서 꺼낸 날짜의 차이가 있는 경우만 갱신
if (dayMax < poll.day) {
dayMax = poll.day;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int xf = poll.x + dx[i];
int yf = poll.y + dy[i];
// 방문을 하지 않았고 다음 탐색하려는 곳이 토마토가 없는 경우가 아닌 경우
if (xf >= 0 && xf < N && yf >= 0 && yf < M && !visited[xf][yf] && tomatoBox[xf][yf] != -1) {
visited[xf][yf] = true;
tomatoBox[xf][yf] = 1;
q.add(new Point(xf, yf, poll.day + 1));
}
}
}
return dayMax;
}
}
4. 배운점
- bfs의 개념을 다시 잡는 계기가 됨
- bfs에서 동시에 진행되는 경우가 있는 경우 q에 넣어서 처리하자
- 필요한 Collection만 선언하여 사용하자
5. 점수
85/100